Halifax is now allowing first-time buyers to take out a 100% mortgage, but they'll need a helping hand from a family member.
The new Family Boost mortgage is the latest guarantor product on the market, and could prove an attractive option for parents willing to lock up their savings to help their child get on to the property ladder.
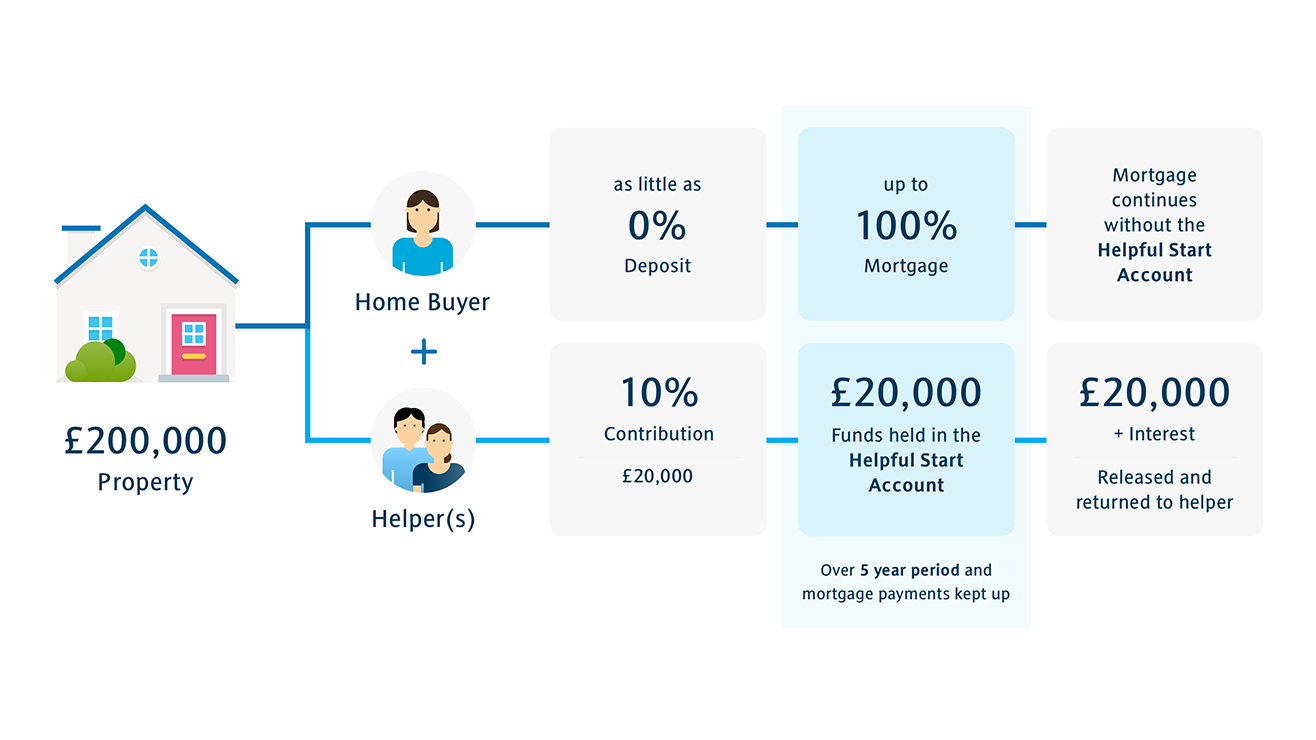
A family deposit mortgage can help boost a first timer buyer's deposit without a family member donating the money directly. By depositing money into an account linked to the borrower's mortgage, a.
- Watch our latest TV ad. The new Family Boost Mortgage. Halifax makes it happen.
- Use your family or friend's savings to buy your own house with your own mortgage – and they'll get their money back, with interest. You don't need a borrower deposit You can borrow the full purchase price of your home because your helper provides 10% as security for five years 1. You could borrow.
- Mortgage Refinancing Boost is here to study your current financial standing and provide expert financial solutions on large purchases, investments + leveraging home equity in various ways to your benefit.
- Halifax Family Boost MortgageWelcome to this weeks two minute Tuesday!In this video, Alex Kerr a qualified Mortgage Broker, discusses the Halifax Family Boos.
Family Boost Mortgage Money Saving Expert
Here, we take a look at the pros and cons of the Halifax deal, and offer advice on taking out a guarantor mortgage.
Halifax launches ‘Family Boost' mortgage: how does it work?
The new deal from Halifax allows first-time buyers to borrow up to 100% of the value of a property, removing the need for an upfront deposit.

There is a catch, however. The borrower will need a family member to put up to 10% of the purchase price in a savings account, which they won't be able to access for three years.
During this three-year period, the money will live in a special Halifax savings account, where it'll earn 2.5% interest.
The new mortgage is available to buyers in England and Wales and applicants can borrow a maximum of £500,000.
If your child stops paying the mortgage, the full amount of savings could be at risk.
The difference between no-deposit deals and 100% mortgages
There's been lots of talk about the possible return of the 100% mortgage over the past year or so. However, it's still the case that no lender has launched a true 100% deal since the financial crash a decade ago.
Since then, all so-called ‘no-deposit' mortgages have required some form of guarantee from a parent or family member, with either savings or property as collateral, as with the Halifax deal.


New guarantor mortgage products are just one way lenders are innovating to attract more first-time buyers.
In the last year, we've seen banks launching mortgages with fixed terms of up to 15 years, ‘professional mortgages' that allow people with specific jobs to take out bigger loans, and an increase in the number of deals offering cashback to people with small-deposits.
Guarantor mortgages: what are my options?
Guarantor mortgages generally fall into one of the three categories below.
Family Boost Mortgage Nationwide
Rates, repayment terms and borrowing limits vary significantly on these products, but here's an overview of how they work.
Savings as security
These deals involve a parent or family member (the guarantor) locking up their savings as collateral. Savings are at risk if the child fails to meet their mortgage payments.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Barclays, Family Building Society, Halifax, Lloyds, Loughborough, Mansfield, Marsden, Saffron, Tipton.
- How much will the guarantor need to deposit? Common amounts include 5% (Saffron), 10% (Barclays, Lloyds, Halifax) or 20% (Mansfield, Marsden, Loughborough) of the purchase price.
- When will they get their money back? After three (Lloyds, Barclays, Halifax), five (Saffron) or seven (Mansfield) years. Some lenders instead release the cash once the amount saved has been paid off the mortgage, or the overall loan-to-value on the mortgage drops to a specific level.
- Will the guarantor get interest on their savings? Usually, yes. Lloyds and Halifax (2.5%) and Barclays (2.25%) pay the highest rates.
- Which mortgage types are available? Three and five-year fixes, some lenders also offer discount deals.
The new Halifax deal pays a joint market-leading interest rate to parents when they lock up their money for three years. This rate is impressive, given that market-leading three-year savings accounts currently only pay up to 2.45% interest.
These deals can make sense for parents who want to maintain some control over their cash (rather than gift a deposit), and see their investment grow over time.
The trade off to this is that guarantor mortgages usually have higher interest rates than standard 90% mortgages. This means the child's monthly repayments can be more expensive than if they were gifted the cash and took out a conventional deal.
Property as security
The guarantor has a charge secured on their property, which can be called in if the child defaults on their mortgage.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Aldermore, Bath, Buckinghamshire, Family Building Society, Loughborough, Marsden, Mansfield, Nationwide, Post Office Money, Tipton.
- Is the parent's home at risk? Most lenders secure a charge of 20% of the value of the new property on the parent's home, though Post Office Money uses a charge of 10%.
- When is the charge released? This varies from lender to lender. For example, Aldermore sets a maximum guarantee period of 10 years.
Alternatively, parents can use their home as security for their loan.
Lenders will usually secure a charge of around 20% of the new property's value on the parent's home. To be eligible, the parent will need to own a specific amount of equity in their home (or in some cases, own their home outright).
These deals are an option for parents who can't or don't wish to offer cash to their child, but with the significant caveat that their home is at risk if their child defaults on the mortgage.
Savings to offset mortgage
The guarantor puts savings into an account, which are then offset against the balance of the child's mortgage.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Family Building Society and Vernon.
- How much will the guarantor need to deposit: 20% with Vernon, or a minimum of £5,000 with Family Building Society.
- When does the guarantor get their money back? As long as mortgage payments are up-to-date, Vernon will release the savings after four years.
- Will the guarantor get interest on their savings? Interest won't be paid as the savings will be used to offset interest on the child's mortgage.
Family offset mortgages work like this: if a child takes out a mortgage for £100,000 and the family member deposits £20,000 on savings into an account, the child only needs to pay interest on £80,000 of the loan.
The upside of these deals is that only the parent's savings are at risk, rather than their home. The downside is that the parent will be locking away their savings for a number of years without earning any interest.
JBSP mortgages: an alternative to guarantor deals
- Which banks offer these deals? Barclays, Buckinghamshire, Clydesdale, Furness, Hinckley & Rugby, Market Harborough, Metro, Tipton & Coseley.
Joint borrower, sole proprietor (JBSP) mortgages are an increasingly popular alternative to a guarantor or joint mortgage.

These deals involve a parent and child taking out a mortgage together, but only the child being named on the property's deeds.
This helps parents avoid the additional stamp duty they'd need to pay if they took out a joint mortgage, and means they won't need to put up savings or a property as security, as with a guarantor mortgage.
JBSP mortgages come with strict criteria, however. The parent will need to have their financial circumstances assessed, and older parents may find themselves ineligible for a normal mortgage term of 25 years.
Choosing a guarantor mortgage: five tips for parents
There is a catch, however. The borrower will need a family member to put up to 10% of the purchase price in a savings account, which they won't be able to access for three years.
During this three-year period, the money will live in a special Halifax savings account, where it'll earn 2.5% interest.
The new mortgage is available to buyers in England and Wales and applicants can borrow a maximum of £500,000.
If your child stops paying the mortgage, the full amount of savings could be at risk.
The difference between no-deposit deals and 100% mortgages
There's been lots of talk about the possible return of the 100% mortgage over the past year or so. However, it's still the case that no lender has launched a true 100% deal since the financial crash a decade ago.
Since then, all so-called ‘no-deposit' mortgages have required some form of guarantee from a parent or family member, with either savings or property as collateral, as with the Halifax deal.
New guarantor mortgage products are just one way lenders are innovating to attract more first-time buyers.
In the last year, we've seen banks launching mortgages with fixed terms of up to 15 years, ‘professional mortgages' that allow people with specific jobs to take out bigger loans, and an increase in the number of deals offering cashback to people with small-deposits.
Guarantor mortgages: what are my options?
Guarantor mortgages generally fall into one of the three categories below.
Family Boost Mortgage Nationwide
Rates, repayment terms and borrowing limits vary significantly on these products, but here's an overview of how they work.
Savings as security
These deals involve a parent or family member (the guarantor) locking up their savings as collateral. Savings are at risk if the child fails to meet their mortgage payments.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Barclays, Family Building Society, Halifax, Lloyds, Loughborough, Mansfield, Marsden, Saffron, Tipton.
- How much will the guarantor need to deposit? Common amounts include 5% (Saffron), 10% (Barclays, Lloyds, Halifax) or 20% (Mansfield, Marsden, Loughborough) of the purchase price.
- When will they get their money back? After three (Lloyds, Barclays, Halifax), five (Saffron) or seven (Mansfield) years. Some lenders instead release the cash once the amount saved has been paid off the mortgage, or the overall loan-to-value on the mortgage drops to a specific level.
- Will the guarantor get interest on their savings? Usually, yes. Lloyds and Halifax (2.5%) and Barclays (2.25%) pay the highest rates.
- Which mortgage types are available? Three and five-year fixes, some lenders also offer discount deals.
The new Halifax deal pays a joint market-leading interest rate to parents when they lock up their money for three years. This rate is impressive, given that market-leading three-year savings accounts currently only pay up to 2.45% interest.
These deals can make sense for parents who want to maintain some control over their cash (rather than gift a deposit), and see their investment grow over time.
The trade off to this is that guarantor mortgages usually have higher interest rates than standard 90% mortgages. This means the child's monthly repayments can be more expensive than if they were gifted the cash and took out a conventional deal.
Property as security
The guarantor has a charge secured on their property, which can be called in if the child defaults on their mortgage.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Aldermore, Bath, Buckinghamshire, Family Building Society, Loughborough, Marsden, Mansfield, Nationwide, Post Office Money, Tipton.
- Is the parent's home at risk? Most lenders secure a charge of 20% of the value of the new property on the parent's home, though Post Office Money uses a charge of 10%.
- When is the charge released? This varies from lender to lender. For example, Aldermore sets a maximum guarantee period of 10 years.
Alternatively, parents can use their home as security for their loan.
Lenders will usually secure a charge of around 20% of the new property's value on the parent's home. To be eligible, the parent will need to own a specific amount of equity in their home (or in some cases, own their home outright).
These deals are an option for parents who can't or don't wish to offer cash to their child, but with the significant caveat that their home is at risk if their child defaults on the mortgage.
Savings to offset mortgage
The guarantor puts savings into an account, which are then offset against the balance of the child's mortgage.
- Which lenders offer these deals? Family Building Society and Vernon.
- How much will the guarantor need to deposit: 20% with Vernon, or a minimum of £5,000 with Family Building Society.
- When does the guarantor get their money back? As long as mortgage payments are up-to-date, Vernon will release the savings after four years.
- Will the guarantor get interest on their savings? Interest won't be paid as the savings will be used to offset interest on the child's mortgage.
Family offset mortgages work like this: if a child takes out a mortgage for £100,000 and the family member deposits £20,000 on savings into an account, the child only needs to pay interest on £80,000 of the loan.
The upside of these deals is that only the parent's savings are at risk, rather than their home. The downside is that the parent will be locking away their savings for a number of years without earning any interest.
JBSP mortgages: an alternative to guarantor deals
- Which banks offer these deals? Barclays, Buckinghamshire, Clydesdale, Furness, Hinckley & Rugby, Market Harborough, Metro, Tipton & Coseley.
Joint borrower, sole proprietor (JBSP) mortgages are an increasingly popular alternative to a guarantor or joint mortgage.
These deals involve a parent and child taking out a mortgage together, but only the child being named on the property's deeds.
This helps parents avoid the additional stamp duty they'd need to pay if they took out a joint mortgage, and means they won't need to put up savings or a property as security, as with a guarantor mortgage.
JBSP mortgages come with strict criteria, however. The parent will need to have their financial circumstances assessed, and older parents may find themselves ineligible for a normal mortgage term of 25 years.
Choosing a guarantor mortgage: five tips for parents
- Take independent financial advice: Acting as a guarantor involves risking either your money or your property, so you'll need to ensure you're in a suitable position to make such a decision. Consider taking independent financial advice and speak to a mortgage broker about which type of deal might be right for you and your child.
- Consider the cost for both parties: As well as the impact on your property or savings, think about the cost of a guarantor mortgage for your child. Guarantor deals often have higher interest rates than standard residential products, so it's important to ensure your child isn't over-stretching their finances.
- Look at other deals and schemes first: A guarantor mortgage might seem attractive at face value, but it's not right for everyone. Ensure your child properly assesses the pros and cons of other first-time buyer options, such as 95% mortgages and the Help to Buy scheme.
- Think about what you want to do with your cash: The big question with guarantor mortgages is ‘do you want to invest your money or gift it to your child?'. If the answer is the former, Halifax's new mortgage could be a decent option. If you're willing to gift the cash to your child, you might be better avoiding guarantor mortgages altogether.
- Consider your relationship with your child: Taking on one of these deals with your child is a big commitment, and if it goes wrong it could affect your relationship in the future. Weigh up the pros and cons of taking this risk before you rush in.
First-time buyer deposits have risen by an extraordinary 52 percent in the last decade.
That means newcomers to home ownership will have to find the biggest deposit since 2009.
However, despite the rising cost of becoming a homeowner, the number of newbies purchasing their first home has more than doubled in the same time period.
New data from the Halifax revealed there have been more than 170,000 first-time buyers in 2019, more than double the 72,180 first-time buyers in 2009.
According to the lender, the average deposit for a first-time buyer is now £41,099, up 52 percent from 2009's £27,059.
Meanwhile, in London, the average first-time buyer must produce a deposit of £101,389, almost double 2009's deposit of £50,944.
To help more first-time buyers realise their dream of home ownership, the Halifax has launched its Family Boost mortgage, which aims to help first-time buyers who don't have a deposit.
The Family Boost mortgage comes with a three-year fixed repayment rate of 2.90 percent and will allow savings from parents or other family to provide security for 10 percent of the overall loan required to buy a property.
Borrowers will pay no fee to access this mortgage, while the family or friends using their savings as a deposit will receive a fixed interest rate of 2.5 percent for the same period.
At the end of three years, the savings and interest will be returned to the family member so long as the mortgagee has kept up to date with repayments.
Russell Galley, managing director of Halifax, said: 'While increasing numbers of first-time buyers is good news for the housing market - and they are not far off the peak of the last boom, which was just under 190,000 in 2006 - it's saving enough to get a foot in the door that's still the biggest blocker.
'As part of our commitment to lending £30 billion to first-time buyers by 2020, we are offering families a way to help give the next generation the boost they need to get on to the property ladder, while providing competitive rates to both buyer and supporter.'
According to the Halifax, the average age of a first-time buyer is 31, up from 30 a decade ago.

